IVF-ET
In Vitro Fertilization, originally developed to treat infertility caused by blocked or damaged fallopian tubes, is currently used to treat a variety of infertility problems. With IVF, the eggs and sperm are collected and mixed together in a laboratory dish so that fertilization occurs outside the body. Several days later, the developing embryo is transferred to the woman's uterus where implantation occurs.
IVF can be used to treat many infertility problems either present singly or in combination. These include obstructed or damaged fallopian tubes, severe male factor that natural fertilization can hardly occur, advanced endometriosis, or unexplained infertility that has not responded to other treatments such as IUI.
IVF in Maria
- The Maria Infertility Clinic is an independent, private center devoted to the diagnosis and treatment of infertility exclusively. All the procedures are individualized, patient oriented, and highly sophisticated, but are also affordable.
- We have seven branch clinics in many parts of Korea. Presently, they are working in seven major cities; Incheon, Ilsan, Pyungchon, Daejeon, Daegu, Busan, and Jeju. All of them are equally successful by using the same technique and culture systems as Seoul.
- Repeated blood sampling in IVF program is not required in the Maria Fertility Clinic, which cuts down your burden of expense and stress.
- We have succeeded in natural cycle IVF for the first time in the Asian countries. With a natural cycle IVF, a single egg is used from the woman’s natural cycle instead of gonadotropin stimulation.
- The Maria Fertility Clinic is the first center of blastocyst transfer and the largest in number in Korea. We have the best culture system for blastocyst.
In VITRO FERTILIZATION
In vitro fertilization(IVF) is a highly successful assisted reproductive technology. There are four basic steps in an IVF treatment cycle:
-
 Step 1. Monitoring of the ovarian follicles and ovulation indcution
Step 1. Monitoring of the ovarian follicles and ovulation indcutionAccording to the baseline ultrasound scan, patients may be got with the most suitable IVF program.
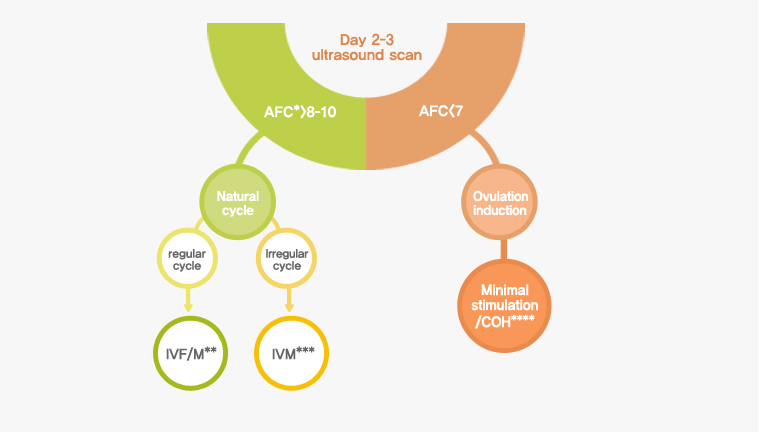
- *AFC: antral follicle count
- ** IVF/M: In vitro fertilization/maturation
- *** IVM: In vitro maturation
- ****COH: controlled ovarian hyperstimulation
- Fig.1. Selection of patients
-
1) Natural cycle IVF/M and IVM
Immature oocyte retrieval followed by in vitro maturation(IVM) technique is suitable for some patients who have many antral follicles. After baseline ultrasound, transvaginal ultrasound scans are going to be repeated on day 7-9. And it will be repeated at 1-3 day intervals until the leading follicle reaches a proper diameter or the endometrial thickness is acceptable.
-
2) Ovulation Induction
Woman who has <7 antral follicles begins taking fertility medications to encourage development of eggs within the ovaries. These medications stimulate the follicles to produce more than one egg in a cycle. Ultrasound examinations to assist in predicting the time of expected ovulation.
-
 Step 2. Egg Retrieval and sperm preparation
Step 2. Egg Retrieval and sperm preparationEgg retrieval from the ovary may occur just prior to the expected time of ovulation. A small needle will be passed directly into the ovary containing follicles via an ultrasound-guided puncture. This technique is performed on an outpatient basis under intravenous sedation and analgesia. During the egg retrieval, the male partner provides a semen sample. The sample is delivered to the lab where it undergoes a clarifying process.
-
 Step 3. Fertilization
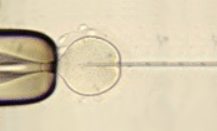
Step 3. FertilizationMixing the egg and sperm together (conventional insemination) to allow fertilization to occur. Certain circumstances may exist to predict that eggs are unlikely to become fertilized using conventional technique. In these cases, a procedure called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is used. Sperm are specially prepared and then individually injected into an egg by means of a microscopic glass needle. This technique greatly increases the chances that the eggs will be fertilized and can help overcome fertilization defect. In general, immature oocytes will be obtained in natural cycle IVF/M and IVM. After egg retrieval, they are going to be transferred into an organ culture dish containing media to help the egg mature. In vitro matured oocytes will be inseminated by ICSI for fertilization.
-
 Step 4. Embryo Transfer
Step 4. Embryo TransferEmbryo transfer is a simple procedure that does not require anesthesia. The selected embryos are inserted into a thin tube and guided toward the female's uterus, where it is hoped they will continue their natural fetal development. Transfer typically takes place three days after egg retrieval, or five to six days after retrieval in the case of blastocyst transfer.
FAQ
-
In Vitro Fertilization, originally developed to treat infertility caused by blocked or damaged fallopian tubes, is currently used to treat a variety of infertility problems. With IVF, the eggs and sperm are collected and mixed together in a laboratory dish so that fertilization occurs outside the body. Several days later, the developing embryo is transferred to the woman's uterus where implantation can occur, resulting in pregnancy.
-
IVF can be used to treat many infertility problems either present singly or in combination. These include obstructed or damaged fallopian tubes, severe male factor that natural fertilization can hardly occur, advanced endometriosis, or unexplained infertility that has not responded to other treatments such as IUI.
-

1) GnRH agonist
In most cases, about 7~10days before your IVF cycle, GnRH-agonist will be commenced and continued until the day of HCG mjection. This medication prevents premature ovulation, which would result in cancellation of the cycle. In case of short protocol, this medication will be commenced from the 2nd day of period.
2) Gonadotropin
Daily injection of gonadotropins is started after two weeks of GnRH-agonist or the 3rd day of period. Gonadotropins help a number of follicles grow simultaneously. The number of follicles can vary from one or two to over 30 in some women. The dose of gonadotropin is based on a prediction of how the ovaries will respond, which varies individually. With baseline vaginal ultrasound, the ovaries are examined for the existence of ovarian cysts. You will be ultrasound scanned to monitor the growth of follicles.
3) HCG
The HCG injection allows the eggs to undergo maturation so that they will be mature when they are retrieved. It is critical that this medication is taken of the assigned time(around 8 P.M) given to you. Ovum pick-up is performed about 36 hours after hCG injection.
4) Collecting the sperm & the eggs
The husband will be asked to collect the sperm sample by masturbation on the day of the ovum pick-up. During ovum pick-up, the eggs are removed from the ovaries. This procedure requires an injection of local anesthetic into the wall of the vagina. We also administer a sedative to make the individual more comfortable. You will not be completely asleep, but sort of in a twilight state. A needle is placed through the wall of the vagina and into the ovary, where the follicles are emptied of their liquid and their eggs. The follicular fluid are collected into a test tube, and passed to an embryologist, who prepares the eggs for insemination. The whole procedure takes less than 15 minutes, and discomfort is generally minimal. You will feel some pelvic heaviness, soreness, or cramping during the procedure. There is often a small amount of bleeding from the wall of the vagina. Most women are able to go home within 1 hour of the procedure. The eggs are then inseminated, meaning that they are mixed with a sperm sample. After fertilization, the embryo can begin developing into 4 to 8 cells or even blastocysts. From the day of ovum pick-up, progesterone is administered by injection or into vagina. This continues daily until the day of pregnancy test (and for four more weeks in case of pregnancy).
5) Embryo transfer
Depending on the quality of the embryos, they may be transferred into the uterus either 2 or 5 days after ovum pick-up. Two days after the OPU you will be contacted by telephone and appointment will be made for the embryo transfer procedure. Embryos are placed into the uterus using a soft catheter. This is a simple procedure and requiring no anesthesia or sedation. After the embryo transfer, 2 hours of bed rest is usually recommended but not obligatory. After that you are free to return to your regular activities except strenuous exercises.
6) Pregnancy
Two weeks after the ovum pick-up, you will return for a blood test, called a "beta-hCG ", to see if you are pregnant. You will receive a telephone call in the afternoon on the day of sampling about your results. If the test is positive, you should continue progesterone supplementation and return for a second blood test one week later. An ultrasound examination will be performed after another week. If your test is negative, you have to stop the progesterone supplementation and menstruation will start within several days.
-
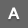
"Long" or "Short" means the duration of GnRH-agonist. The standard regimen in Maria Fertiltiy Clinic is the long protocol in which GnRH-agonist starts 7-10 days before expected menstruation. If you are old-aged or few oocytes were retrieved in previous cycle, short protocol may be better and you would begin GnRH-agonist on second day of the period.
-
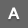
A blastocyst is a highly developed embryo (usually developed five days after fertilization) that has underwent many stages of development. These blastocysts have a higher implantation potential than embryos grown for only three days, and as a result, fewer embryos are needed to achieve the same pregnancy rate, with a lower rate of multiple pregnancy. The transfer of blastocysts is physiological in that the blastocyst synchronize with the uterine endometrium, and facilitates the identification of good quality embryos.
-
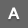
If you have regular period, you should visit 7-10 days before expected menstruation. Otherwise, 2nd or 3rd day of period would be suitable.
-
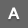
The main risk of gonadotropins is ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). It occurs when too many follicles develop in the ovaries. Ovarian hyperstimulation is characterized by ovarian enlargement, abdominal discomfort, and gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. In severe cases, ascites, pleural or pericardial effusion, hypovolemia, and thromboembolic phenomena can occur. If the ovaries enlarge too much, torsion of the ovaries can occur. Fatalities have been reported in severe cases, but in mild cases, hospitalization is rarely required to regulate the fluid balance.Embryos may be frozen and saved for a later cycle in severe cases. The incidence of multiple pregnancy is about 20% and an ectopic (tubal) pregnancy can occur 2-4% of pregnancies. The rate of spontaneous abortion and congenital anomalies is about the same with non-IVF pregnancies.
-
The success rate is about 35-40% per cycle in general. It depends upon the numbers of eggs or the quality of embryos available for transfer.
-
It will cost about \7~8 million won per 1 cycle. But it could be 8 million won to the maxmum cost because of the dosage and kind of hormone injection, and additional procedures such as ICSI.
-
IVF-ET usage in vitro matured oocytes is recommended for the PCOS patients, who are prone to develope OHSS in response to gonadotropins. The ovum pick-up is usually scheduled between day 8 and day 13 of period without gonadotropin injection, and the semen is collected on the day after the ovum pick-up. ET is perfomed 3~6 days after the ovum pick-up. The procedure and methods of ovum pick-up and embryo transfer are same as conventional IVF.
-
Immature oocyte retrieval followed by in vitro maturation of these oocytes is an attractive infertility treatment. Recent improvement in culture conditions and techniques have led to a great advancement for in vitro matured eggs to produce viable embryos. Compared with ovarian-stimulated IVF, the major advantages of IVM include avoidance of the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, reduced cost, can be repeated monthly, and simplified treatment. If the patient is properly selected, the pregnancy rate is close to that of conventional IVF program.
-
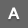
ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) is a micromanipulation procedure in which a sperm is injected directly into the cytoplasm of an egg. It is particularly effective in case of extreme male infertility. ICSI is also used if there is an apparent problem with fertilization in an IVF cycle. In case of "NO" sperm in semen, epididymal or testicular sperm can be used for ICSI procedure. PESA (percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration) is indicated for men with obstructive azoospermia such as absence of vas or failed vasectomy reversal. A small needle is passed directly into the head of the epididymis and the fluid containing sperm is aspirated. In case of non-obstructive azoospermia, the sperm is obtained directly from the testis, which is called TESE (testicular sperm extraction). The retrieved sperms from the fluid or tissues are prepared for ICSI. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
-
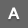
Freezing of extra embryos gives couples an additional opportunity to conceive without undergoing another ovarian stimulation cycle and ovum pick-up. The success rate with frozen/thawed embryos is improved when embryos are frozen at blastocyst stage. The frozen/thawed ET can be applied to the case of severe OHSS, which may be aggravated if pregnancy occurred. If you have regular periods, transfer will be scheduled 4-5 days after ovulation. Otherwise, it can be dated according to the endometrial development with hormonal medications.
-
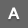
When a woman's ovaries stop functioning prematurely, she is no longer able to produce eggs. In these cases, oocyte donation is the last choice. Donor eggs are fertilized with your partner's sperm and the resulting embryos are placed into your uterus. In Korea, because there's no ovum bank established, relatives, such as sisters, would personally offer their eggs.